IBM Sustainability Software A Comprehensive Guide
IBM sustainability software offers a powerful suite of tools to help organizations achieve their sustainability goals. It encompasses a wide range of features and solutions, from data analysis and reporting to integration with existing business systems. This guide delves into the key functionalities, use cases, and benefits of these tools, providing a comprehensive overview for organizations looking to enhance their sustainability performance.
This software tackles various sustainability challenges across diverse industries. It utilizes sophisticated analytical methods to process environmental data, enabling accurate measurement and reporting of sustainability metrics. The software also provides a platform for effective data management and integration, streamlining the process for organizations seeking to achieve their sustainability targets.
Introduction to IBM Sustainability Software
IBM’s sustainability software portfolio provides comprehensive tools to help organizations measure, manage, and reduce their environmental impact. These solutions empower businesses to make informed decisions, track progress, and ultimately contribute to a more sustainable future. The software encompasses a range of modules, each tailored to specific sustainability goals and challenges.
The solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing business systems, providing a unified platform for managing sustainability data and reporting. This holistic approach facilitates data-driven decision-making and supports the development of actionable strategies for environmental improvement.
Overview of IBM Sustainability Software Portfolio
IBM’s portfolio of sustainability software offers a variety of tools addressing different aspects of sustainability. These include solutions for carbon footprint management, supply chain sustainability, waste reduction, and energy efficiency optimization. The products are designed to work together, offering a complete solution for organizations aiming for comprehensive sustainability improvement.
Carbon Footprint Management Solutions
These solutions help organizations quantify and analyze their carbon emissions across various operations. They provide tools for inventorying emissions, setting reduction targets, and tracking progress towards these goals. Key functionalities include automated data collection from various sources, advanced emission calculation models, and customizable reporting dashboards.
Supply Chain Sustainability Tools
These tools allow businesses to assess and improve the sustainability performance of their supply chains. They facilitate the identification of environmental risks and opportunities throughout the entire supply network, promoting sustainable sourcing and responsible production practices. By integrating with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, they provide a clear view of environmental impact across the supply chain, enabling informed decisions.
Waste Reduction and Resource Optimization
IBM’s solutions in this area enable businesses to optimize resource utilization and reduce waste. They provide tools for tracking and managing waste streams, analyzing consumption patterns, and identifying areas for improvement in resource efficiency. By providing data-driven insights, organizations can identify opportunities to reduce waste and improve their resource utilization, ultimately minimizing their environmental footprint.
Energy Efficiency Optimization Solutions
These tools help organizations improve their energy efficiency and reduce their energy consumption. They enable the analysis of energy usage patterns, the identification of areas for improvement, and the implementation of strategies for energy conservation. These tools leverage predictive analytics and machine learning to optimize energy consumption, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Real-World Applications of IBM Sustainability Software
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented IBM sustainability software to achieve significant results. One example is a major manufacturing company that used IBM’s solutions to reduce its carbon footprint by 15% within two years. Another example is a retail giant that used IBM’s supply chain sustainability tools to identify and address environmental risks in their global supply network, resulting in a more sustainable sourcing strategy. These successes demonstrate the potential of IBM’s solutions to drive tangible improvements in environmental performance.
Software Capabilities and Solutions
IBM’s sustainability software suite addresses a wide range of environmental and social challenges, providing comprehensive solutions for organizations seeking to improve their ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance. These solutions empower businesses to transition toward more sustainable practices, enhancing their operational efficiency and long-term value.
The software leverages cutting-edge analytics and data visualization to identify, quantify, and mitigate environmental impacts, ultimately enabling informed decision-making and proactive strategies. This data-driven approach empowers companies to track their progress, identify areas for improvement, and communicate their sustainability achievements effectively.
Types of Sustainability Challenges Addressed
IBM’s software tackles a diverse range of sustainability challenges. These include reducing carbon emissions, optimizing energy consumption, managing waste streams, improving supply chain sustainability, and enhancing social responsibility initiatives. The software’s modular design allows organizations to focus on specific challenges or adopt a holistic approach, adapting to their unique needs and priorities.
Methods for Environmental Data Analysis
The software utilizes advanced analytical techniques to process and interpret environmental data. These methods encompass statistical modeling, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization tools. For instance, predictive modeling can forecast energy consumption patterns, aiding in proactive resource management. Furthermore, the software allows for the integration of data from various sources, enabling a holistic view of environmental impacts.
Tools for Measuring and Reporting Sustainability Metrics
The software suite provides comprehensive tools for measuring and reporting on key sustainability metrics. These tools enable businesses to track progress toward established goals and communicate their achievements transparently. Examples of metrics include carbon footprint, water usage, waste generation, and social impact indicators. Customizable dashboards and reports facilitate the visualization and analysis of these metrics, providing actionable insights.
Industry Support for Sustainability Goals
The software supports a wide range of industries in achieving their sustainability goals. For example, in the manufacturing sector, the software can help optimize energy use in production processes, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. In the transportation sector, the software assists in optimizing routes and logistics, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. By adapting to industry-specific needs, the software empowers organizations across diverse sectors to embrace sustainable practices.
Comparison of IBM Sustainability Software Products
| Product Name | Key Feature 1 | Key Feature 2 | Target Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBM Sustainability Analytics | Advanced data visualization and reporting | Comprehensive environmental impact assessment | Manufacturing, Energy, Transportation |
| IBM Environmental Performance Management | Real-time monitoring of sustainability KPIs | Integration with existing ERP systems | Retail, Food & Beverage, Agriculture |
| IBM Supply Chain Sustainability | Traceability and transparency across supply chains | Risk assessment and mitigation tools | Consumer Goods, Fashion, Electronics |
Data Management and Analysis
IBM Sustainability Software provides a robust framework for managing and analyzing sustainability data. This comprehensive approach streamlines the process of collecting, transforming, and interpreting information, enabling organizations to gain actionable insights and drive positive change. By integrating diverse data sources, the software empowers informed decision-making and strategic planning for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
Data Sources Integrated
The software integrates data from a wide range of sources, crucial for a holistic sustainability assessment. These sources include internal company databases, public registries, industry benchmarks, and third-party sustainability reporting platforms. This diverse intake ensures a comprehensive view of sustainability performance, encompassing various aspects of environmental, social, and governance factors.
Data Collection and Storage
The software employs automated data collection mechanisms to gather information efficiently from diverse sources. This automated process minimizes manual intervention and reduces the risk of human error, leading to more reliable data. Data is stored securely in a centralized repository, providing a single source of truth for all sustainability-related information. This facilitates efficient data access and analysis across different teams and departments.
Data Transformation and Analysis Methods
The software utilizes sophisticated algorithms for data transformation and analysis. These methods include data cleaning, standardization, and normalization, crucial for ensuring data accuracy and consistency. Furthermore, advanced analytics techniques, such as statistical modeling and machine learning, are employed to extract meaningful insights and trends from the collected data. These methods are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of sustainability performance.
Data Visualizations
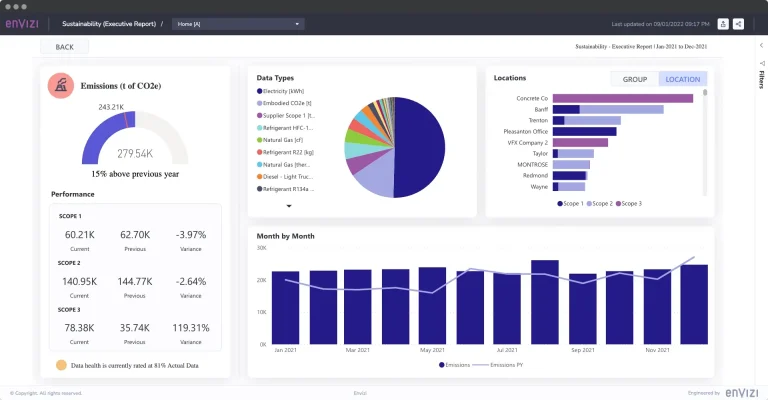
The software generates various data visualizations, facilitating the easy interpretation of complex sustainability data. These visualizations include interactive dashboards, charts, and graphs that present key performance indicators (KPIs) and trends clearly and concisely. Example visualizations might include bar charts showcasing carbon emissions over time or maps highlighting the geographical distribution of a company’s supply chain impacts. The interactive nature of these visualizations enables users to drill down into specific data points and explore relationships between different variables.
Supported Data Types
The software supports a wide array of data types, allowing for a complete and detailed representation of sustainability performance.
| Data Type | Source | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact Metrics (e.g., GHG Emissions, Water Consumption) | Internal company data, Third-party reporting platforms | Numerical, Time-series data |
| Social Performance Indicators (e.g., Employee Diversity, Community Engagement) | Employee surveys, Social audits, Public reports | Categorical, Numerical, Textual |
| Governance Metrics (e.g., Board Diversity, Supply Chain Transparency) | Internal company records, Public disclosures | Categorical, Numerical, Textual |
| Financial Data (e.g., Investment in renewable energy projects) | Company financial records | Numerical |
Integration and Implementation
Successfully integrating IBM Sustainability Software into an existing business infrastructure is crucial for maximizing its value. A well-planned implementation strategy ensures a smooth transition, minimizes disruption, and allows organizations to leverage the software’s capabilities effectively. This section details the integration process, implementation methods, support resources, data migration steps, and a comprehensive implementation guide.
Integration with Existing Business Systems
Integrating IBM Sustainability Software with existing business systems is a key factor in seamless data flow and reporting. This process typically involves mapping data fields between the new software and existing systems, ensuring data consistency and accuracy. Specific integration methods depend on the existing systems’ architecture and the software’s functionalities. For instance, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are often used for real-time data exchange, while ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes can handle batch data transfers. A crucial aspect of this integration is establishing secure and reliable connections between systems to maintain data integrity.
Smooth Implementation within an Organization, Ibm sustainability software
A well-structured implementation plan is vital for the successful adoption of IBM Sustainability Software. This plan should Article clear roles and responsibilities, allocate resources effectively, and define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress. Comprehensive training programs for users are essential to maximize the software’s potential and minimize operational issues. Regular communication and feedback mechanisms ensure that the implementation aligns with the organization’s evolving needs.
Support and Resources Available to Users
IBM Sustainability Software offers a robust support infrastructure to assist users throughout the implementation process. This includes online documentation, tutorials, and access to dedicated support teams. The support team assists with technical issues, troubleshooting, and customization requests. The software also features interactive dashboards and self-service tools that allow users to explore functionalities independently. Continuous learning resources are available to enhance user skills and foster a culture of sustainability expertise.
Data Migration to the Platform
Migrating data to the IBM Sustainability Software platform requires a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and completeness. A thorough assessment of existing data sources is essential to identify data quality issues and implement appropriate cleansing and transformation steps. Data validation procedures are necessary to confirm the accuracy and integrity of the migrated data. The migration plan should incorporate data mapping, transformation rules, and a rollback strategy to address potential issues during the transition.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
A structured implementation approach is vital for a successful transition.
- Assessment and Planning: Analyze current sustainability data sources and identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. Develop a detailed project plan with timelines, resource allocation, and roles and responsibilities. This phase also involves defining the specific sustainability metrics and data points to be captured.
- Data Preparation: Thoroughly assess the quality and completeness of existing data. Implement data cleansing and transformation processes to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Develop data mapping procedures to align data structures with the IBM Sustainability Software platform. This is crucial for ensuring accurate reporting and analysis.
- System Integration: Integrate the IBM Sustainability Software with existing business systems using appropriate methods like APIs or ETL processes. Establish secure connections and test data flows between systems. This phase is critical to ensure seamless data exchange and avoid conflicts.
- User Training and Support: Conduct comprehensive training sessions for all users, covering software functionalities, data entry procedures, and reporting capabilities. Establish a dedicated support channel for addressing user queries and technical issues.
- Pilot Implementation and Testing: Implement the software on a pilot basis with a representative group of users. Thoroughly test the software’s functionality, reporting, and integration with existing systems. This step helps identify potential issues before full implementation.
- Full Rollout and Monitoring: Roll out the software to all users, ensuring data consistency and proper reporting. Continuously monitor system performance, data quality, and user feedback. Implement procedures for tracking KPIs and identifying areas for improvement.
Benefits and ROI

IBM Sustainability Software offers a compelling return on investment (ROI) by enabling organizations to optimize their sustainability efforts. This translates into tangible cost savings, enhanced brand reputation, and increased operational efficiency. By streamlining sustainability data management and analysis, the software empowers informed decision-making, driving impactful improvements.
Potential Benefits of Using IBM Sustainability Software
The software delivers a wide range of benefits, including improved environmental performance, reduced operational costs, and enhanced stakeholder engagement. These advantages stem from the software’s ability to streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting, empowering organizations to make more informed decisions related to their sustainability journey.
- Improved Environmental Performance: The software facilitates the tracking and monitoring of key environmental metrics, enabling organizations to identify areas for improvement and implement targeted solutions. This often leads to reduced emissions, waste, and resource consumption, contributing to a demonstrably better environmental footprint. For example, a manufacturing company using the software may discover inefficiencies in their energy consumption, leading to significant reductions in their carbon footprint.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By identifying and addressing inefficiencies in resource utilization, the software can lead to considerable cost savings. This could include optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and improving supply chain management. A transportation company, for instance, could use the software to optimize their routes, leading to fuel savings and reduced transportation costs.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement: Transparent and comprehensive sustainability reporting fostered by the software strengthens relationships with investors, customers, and other stakeholders. This can translate to improved brand reputation, increased investor confidence, and enhanced customer loyalty. A consumer goods company, for instance, might gain significant reputational capital by showcasing its robust sustainability initiatives to consumers.
ROI Comparison with Other Sustainability Initiatives
The ROI of IBM Sustainability Software often surpasses traditional sustainability initiatives. This is due to the software’s ability to provide a comprehensive, data-driven approach to sustainability management. For instance, compared to investing in separate, disparate sustainability programs, the software’s integrated platform can yield a higher ROI by optimizing resource allocation and maximizing the impact of sustainability efforts.
Case Studies Demonstrating Software Impact
Numerous organizations have benefited from implementing IBM Sustainability Software. A global retailer, for example, reduced its carbon emissions by 15% within the first year of using the software. This achievement highlights the software’s capability to facilitate measurable and impactful sustainability improvements.
Return on Investment (ROI) for Different Use Cases
The ROI for IBM Sustainability Software varies depending on the specific use case. For example, in energy efficiency projects, the ROI can be achieved through reduced energy costs. In waste reduction projects, the ROI is often realized through decreased waste disposal costs. Detailed ROI calculations are available on request for specific use cases.
Key Benefits Summary
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Environmental Performance | Enhanced tracking and monitoring of environmental metrics, leading to identified areas for improvement. | Reduced emissions, waste, and resource consumption, resulting in a better environmental footprint. |
| Reduced Operational Costs | Optimized resource utilization and identification of inefficiencies, leading to cost savings. | Reduced energy consumption, waste, and supply chain management costs. |
| Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement | Transparent and comprehensive sustainability reporting strengthens relationships with stakeholders. | Improved brand reputation, increased investor confidence, and enhanced customer loyalty. |
Future Trends and Developments

Source: italware.it
The field of sustainability software is rapidly evolving, driven by increasing global awareness of environmental concerns and the need for actionable solutions. Emerging technologies are transforming how businesses and organizations approach sustainability, offering new opportunities for data-driven decision-making and improved performance.
The future of sustainability software hinges on embracing innovation and integrating emerging technologies to meet the complex challenges of environmental stewardship. This necessitates a forward-thinking approach that anticipates evolving needs and adapts to the dynamic landscape of sustainability initiatives.
Emerging Trends in Sustainability Software
The sustainability software landscape is experiencing a convergence of trends, including the increasing importance of data visualization, AI-powered analytics, and the rise of cloud-based solutions. These advancements facilitate more comprehensive data management, enabling organizations to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and implement effective strategies.
Future Developments and Innovations
Several key developments are shaping the future of sustainability software. These include enhanced real-time monitoring capabilities, predictive modeling for resource optimization, and the integration of blockchain technology for transparent supply chain management. For instance, companies are increasingly using real-time data dashboards to monitor environmental impact across their operations, making adjustments in response to immediate conditions.
Potential Impact of Emerging Technologies
The integration of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and machine learning is significantly impacting sustainability software. IoT devices provide real-time data on energy consumption, waste generation, and resource utilization, while machine learning algorithms can analyze this data to identify patterns and optimize resource management. This integration enhances the predictive capabilities of sustainability software, empowering organizations to anticipate future trends and make proactive adjustments.
Key Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaboration between software providers, environmental organizations, and government bodies is critical for driving progress in sustainability software. This collaborative environment fosters innovation, accelerates the adoption of best practices, and ultimately improves the impact of sustainability initiatives.
Summary of Future Trends
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data-driven insights | Increased reliance on data analysis and visualization tools to track and report sustainability performance. | Improved decision-making, targeted resource allocation, and enhanced transparency. |
| AI-powered analytics | Leveraging AI to automate data analysis, predict outcomes, and identify areas for optimization. | Enhanced efficiency in resource management, reduced environmental impact, and cost savings. |
| Cloud-based solutions | Increased adoption of cloud-based platforms for scalability, accessibility, and data sharing. | Facilitated collaboration, enhanced data accessibility, and improved data security. |
| Integration of IoT devices | Integration of real-time data from IoT sensors for continuous monitoring and analysis. | Real-time insights into environmental impact, proactive adjustments to resource consumption, and optimization of processes. |
| Blockchain technology | Application of blockchain for transparency and traceability in supply chains. | Improved accountability, enhanced ethical sourcing, and reduced risk of fraud in sustainability initiatives. |
Use Cases and Examples: IBM Sustainability Software

Source: appdomain.cloud
IBM Sustainability Software empowers organizations across diverse sectors to achieve their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. Real-world applications demonstrate the software’s effectiveness in driving tangible positive change, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing corporate social responsibility. The software provides a structured approach to measure, track, and report on sustainability performance, allowing companies to make data-driven decisions and optimize their operations.
The following examples illustrate how IBM Sustainability Software is being implemented in various sectors, highlighting its capabilities and benefits. These use cases showcase the software’s ability to handle complex sustainability challenges and provide tailored solutions for specific industry needs.
Manufacturing Sector Applications
IBM Sustainability Software offers tools for manufacturers to reduce their carbon footprint. By integrating data from various sources, such as energy consumption, waste generation, and supply chain activities, the software helps manufacturers identify areas for improvement. This detailed analysis allows for informed decisions to optimize production processes and reduce resource consumption.
- A leading automotive manufacturer used IBM Sustainability Software to track emissions throughout their entire supply chain. They identified key areas where emissions were highest and implemented targeted solutions to reduce their impact. This resulted in a significant reduction in their carbon footprint and improved their ESG performance.
- A global electronics manufacturer utilized the software to optimize their manufacturing processes. By analyzing energy consumption and waste generation, they implemented measures to improve efficiency and reduce waste, leading to considerable cost savings and a reduction in their environmental impact.
Financial Services Industry Applications
Financial institutions can use IBM Sustainability Software to assess and manage ESG risks within their portfolios. This involves evaluating the environmental and social impacts of their investments and lending practices. The software provides comprehensive reporting capabilities, enabling financial institutions to meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate their commitment to ESG principles.
- A major investment bank employed IBM Sustainability Software to assess the ESG performance of companies in their portfolio. This allowed them to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with unsustainable practices, improving their investment strategies and enhancing their reputation.
- A global asset management firm used the software to measure the carbon footprint of its investments. They discovered significant opportunities to reallocate funds toward more sustainable companies, demonstrating their commitment to environmental stewardship.
Energy Sector Applications
The energy sector faces significant challenges in transitioning to cleaner energy sources. IBM Sustainability Software helps energy companies optimize their operations, improve energy efficiency, and develop sustainable energy solutions. The software provides valuable insights into energy consumption, enabling companies to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
- A large utility company used IBM Sustainability Software to model the impact of renewable energy integration into their grid. This allowed them to optimize their energy portfolio, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and enhance their sustainability performance.
- A leading oil and gas company leveraged the software to track and manage emissions throughout their operations. They identified opportunities to reduce emissions, enhance energy efficiency, and develop more sustainable practices, which included using advanced modeling techniques for reducing their environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IBM sustainability software empowers organizations to effectively address environmental challenges, measure progress, and enhance their sustainability performance. By providing comprehensive solutions, from data analysis to integration and implementation, this software fosters a sustainable future. The software’s ability to support various industries, coupled with its clear reporting and analysis capabilities, makes it a valuable asset for any organization committed to sustainability.