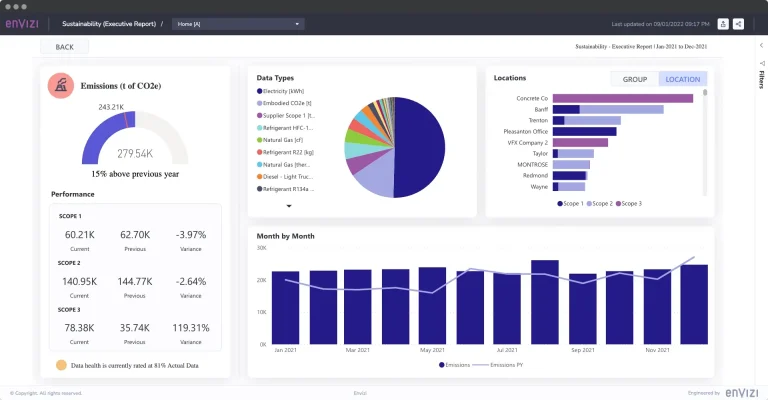
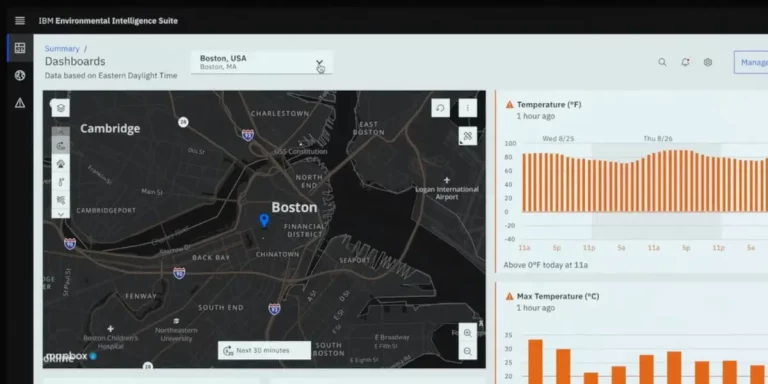
IBM ESG Software A Comprehensive Overview
IBM ESG software provides a powerful suite of tools for organizations to manage their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. This software helps companies track key metrics, analyze data, and report on their ESG initiatives in a streamlined and efficient manner. The software encompasses a wide range of functionalities, from data collection and analysis to reporting and benchmarking. It empowers businesses to enhance their sustainability efforts and meet growing ESG reporting demands.
IBM’s ESG software solutions cater to diverse organizational needs, offering flexible and adaptable tools. The software’s various modules and features address different aspects of ESG, such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. This allows organizations to tailor their ESG strategies and reporting to specific industry standards and requirements. Moreover, the software facilitates data integration with existing enterprise systems, enabling a holistic view of an organization’s performance.
Introduction to IBM ESG Software
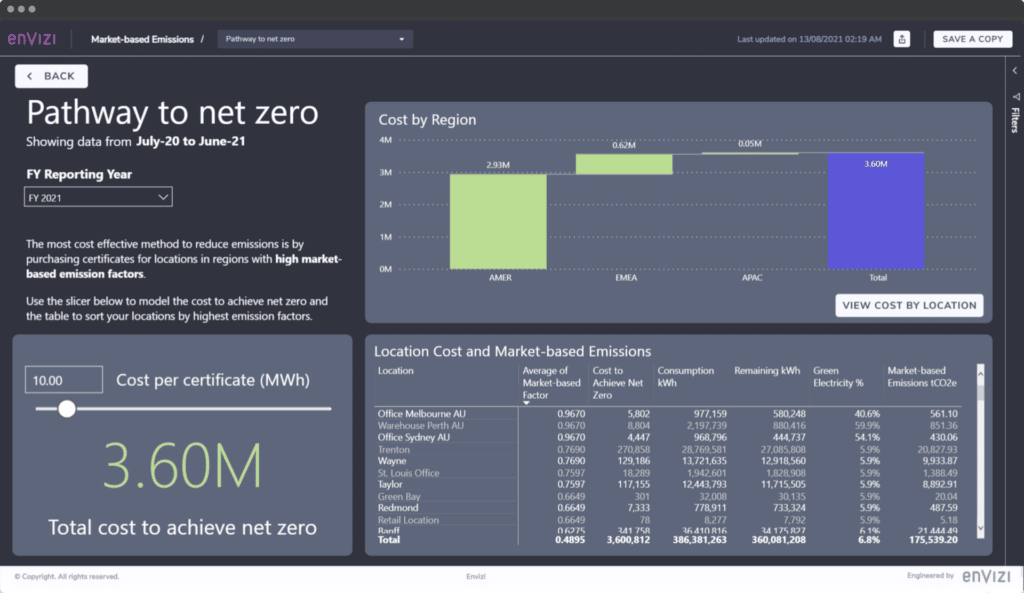
IBM’s ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) software solutions provide comprehensive tools for organizations to assess, manage, and report on their ESG performance. These solutions empower businesses to integrate ESG considerations into their core operations, fostering sustainability and long-term value creation. By providing data-driven insights and actionable strategies, IBM ESG software enables companies to meet evolving regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
Overview of IBM ESG Software Solutions
IBM offers a suite of ESG software solutions designed to address the diverse needs of organizations across various sectors. These solutions encompass a range of functionalities, from data collection and analysis to reporting and stakeholder engagement. The software solutions leverage cutting-edge technologies and methodologies to provide accurate and reliable ESG information. The core objective is to facilitate a seamless integration of ESG principles into the operational fabric of the organization.
Types of ESG Software Offered
IBM’s ESG software portfolio includes modules for environmental impact assessment, social responsibility monitoring, and governance compliance. These modules often integrate with existing business systems, facilitating data flow and analysis. Specific software offerings might include modules for carbon footprint calculation, supplier risk assessment, diversity and inclusion reporting, and ethical sourcing verification.
ESG Data Management Capabilities
IBM ESG software solutions are equipped to handle diverse types of ESG data, including environmental metrics, social impact indicators, and governance practices. Data sources can range from internal company records to external databases and public reports. The software can aggregate, validate, and analyze this data to create a comprehensive ESG profile for the organization. This facilitates data-driven decision-making and performance improvement across various ESG dimensions.
IBM ESG Software Solutions Table
| Software Name | Key Features | Target Audience | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBM ESG Impact Assessment | Comprehensive environmental impact assessment tools, including carbon footprint calculation, renewable energy integration, and supply chain sustainability analysis. | Manufacturing, energy, and transportation companies. | Subscription-based, with tiered pricing based on the number of users and features. |
| IBM ESG Social Responsibility Monitoring | Modules for supplier risk assessment, diversity and inclusion reporting, employee engagement analysis, and community impact measurement. | Companies across various sectors are seeking to enhance their social responsibility practices. | Subscription-based, with flexible options for customized solutions. |
| IBM ESG Governance Compliance | Tools for regulatory compliance, ethical sourcing verification, and corporate governance best practice analysis. | Companies are required to meet specific ESG regulatory standards. | Subscription-based, with varying tiers based on the number of policies and regulatory frameworks. |
Key Features and Capabilities
IBM ESG software provides a comprehensive suite of tools for organizations to manage and enhance their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance. This software empowers businesses to effectively collect, analyze, and report on ESG data, enabling informed decision-making and improved sustainability practices.
The software offers a robust framework for integrating ESG considerations into core business operations. It allows companies to track progress toward ESG goals, identify areas for improvement, and benchmark their performance against industry peers. This integrated approach facilitates a more holistic and data-driven understanding of ESG issues.
Data Collection and Management
The software employs various methods for collecting ESG data, including automated data feeds from internal systems, manual data entry, and integrations with external data sources. This multifaceted approach ensures comprehensive data coverage across diverse ESG aspects. Data validation and cleansing procedures are integrated to maintain data quality and accuracy.
Data Analysis and Reporting
Advanced analytics capabilities facilitate deep dives into ESG data. The software allows for trend analysis, identifying patterns and anomalies in ESG performance over time. This enables businesses to proactively address potential risks and capitalize on opportunities for improvement.
Benchmarking and Performance Tracking
The software offers industry-specific benchmarking capabilities. Users can compare their ESG performance against industry peers and identify areas where they excel or need to improve. This comparative analysis provides valuable insights and fosters continuous improvement in ESG practices. The software tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure ESG performance against predefined targets.
Advanced Analytics Capabilities
Predictive modeling capabilities within the software allow for the forecasting of future ESG trends. This allows businesses to proactively prepare for potential challenges and capitalize on opportunities. The software generates insightful reports that visualize ESG data and provide actionable recommendations. For example, if a company notices a trend towards increasing carbon emissions, the software can identify the source and suggest potential mitigation strategies.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
The software seamlessly integrates with various enterprise systems, such as financial management systems, supply chain management systems, and human resource management systems. This ensures a unified view of ESG data across the organization. Data consistency and reduced manual effort are significant benefits of these integrations.
Reporting Formats and Visualizations
The software offers a variety of reporting formats, including:
| Reporting Format | Visualization |
|---|---|
| Executive Summaries | Interactive dashboards, concise reports |
| Detailed Reports | Trend charts, bar graphs, pie charts |
| Customizable Reports | User-defined layouts, data visualizations |
These formats provide flexible reporting options, allowing businesses to tailor reports to specific stakeholders and purposes. The software also allows for custom visualizations to tailor reports to particular needs. For instance, a company might want to visualize the relationship between employee satisfaction scores and diversity initiatives.
Use Cases and Applications
IBM ESG software empowers businesses to proactively manage their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. By providing a centralized platform for data collection, analysis, and reporting, the software facilitates a more holistic understanding of ESG impacts and helps organizations align their operations with sustainability goals. This allows them to identify areas for improvement, mitigate risks, and enhance their overall sustainability performance.
Real-World Examples of ESG Software Use
Numerous companies across diverse sectors are leveraging IBM ESG software to enhance their sustainability initiatives. For example, a manufacturing company might use the software to track energy consumption across its facilities, identify opportunities for reducing emissions, and report on its progress towards carbon neutrality targets. Similarly, a financial institution might use the software to assess the ESG risks associated with its investment portfolio, identify sustainable investment opportunities, and demonstrate its commitment to responsible finance.
Meeting ESG Compliance Requirements
The software streamlines the process of gathering and reporting ESG data, thereby significantly reducing the administrative burden associated with compliance. The platform’s automated data collection and validation capabilities ensure accuracy and reliability, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. This ensures businesses can confidently meet ESG reporting requirements across various jurisdictions and standards.
Challenges in Managing ESG Data and Solutions
Businesses often face challenges in managing ESG data due to its diverse nature and scattered sources. Data silos, varying reporting formats, and inconsistent data quality can impede effective analysis and reporting. IBM ESG software addresses these issues by providing a unified platform for consolidating ESG data from various sources, standardizing data formats, and ensuring data quality through validation checks. This allows for a more comprehensive and reliable understanding of ESG performance.
Comparison of ESG Reporting Approaches
Different organizations adopt various approaches to ESG reporting, ranging from basic disclosures to comprehensive sustainability reports. The software provides flexibility in tailoring reporting to meet specific needs, supporting both basic compliance reporting and detailed sustainability disclosures. It allows businesses to adapt their reporting approach based on their specific goals and stakeholder expectations. This flexibility ensures that the software adapts to various reporting formats, standards, and needs.
Industries and Use Cases for IBM ESG Software
The table below illustrates diverse industries and their use cases for IBM ESG software. These examples demonstrate the software’s applicability across different sectors, highlighting its ability to enhance sustainability performance and meet compliance requirements.
| Industry | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Tracking energy consumption, reducing emissions, achieving carbon neutrality targets, and enhancing supply chain sustainability. |
| Financial Services | Assessing ESG risks in investment portfolios, identifying sustainable investment opportunities, and demonstrating commitment to responsible finance. |
| Retail | Improving product lifecycle assessment, reducing waste in operations, and promoting ethical sourcing. |
| Technology | Reducing carbon footprint from operations, promoting diversity and inclusion, and adhering to ethical data practices. |
| Energy | Transitioning to renewable energy sources, optimizing energy efficiency, and enhancing sustainability in the supply chain. |
Data Management and Reporting
IBM ESG software provides a robust framework for managing and reporting environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data. This comprehensive system facilitates the collection, validation, and analysis of ESG information, ultimately enabling organizations to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and communicate their ESG performance transparently. It offers a structured approach to data management, ensuring accuracy and consistency across the entire ESG reporting process.
Data Collection Methods
The software employs various data collection methods, leveraging diverse data sources and integrations. This approach ensures comprehensive data capture. Primary data sources often include internal databases, operational systems, and survey results. Secondary data sources, such as publicly available reports and industry benchmarks, supplement the internal data. The software supports integrations with a wide range of third-party platforms, streamlining data ingestion and eliminating manual data entry. This integrated approach minimizes data silos and enhances the accuracy of the overall ESG reporting.
Data Validation and Cleansing
Data validation and cleansing processes are crucial components of the software’s data management system. The system includes automated checks to identify inconsistencies, errors, and outliers in the collected data. These checks ensure data integrity and reliability and enhance the accuracy of subsequent analyses and reporting. Data cleansing procedures remove redundant or inaccurate data, further enhancing the quality of the ESG data. This rigorous approach ensures that the data used for reporting and decision-making is dependable.
Reporting Options
The software provides a wide array of reporting options to visualize and communicate ESG performance. These options range from standard reports summarizing key metrics to interactive dashboards tailored to specific stakeholder needs. Standard reports offer a concise overview of performance against pre-defined ESG targets, providing a clear picture of overall progress. Customizable dashboards allow users to visualize data in a format that best suits their specific needs and priorities. This flexibility enables organizations to tailor reports to communicate effectively with different stakeholders.
Customizable Dashboards and Reports
The software empowers users to create highly customized dashboards and reports tailored to specific needs and preferences. This capability enables organizations to analyze data from various perspectives, including by geography, industry, or specific ESG criteria. Users can select specific metrics and indicators to focus on and arrange the information on the dashboard to best meet their needs. This level of customization facilitates a deep understanding of ESG performance, aiding in identifying areas for improvement. For example, a company can create a dashboard focused on supply chain sustainability, showcasing the carbon footprint of different suppliers.
Comparison of ESG Software Data Management Capabilities
| Software Solution | Data Sources Supported | Data Validation Methods | Reporting Options | Customization Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBM ESG Software | Internal databases, operational systems, surveys, public reports, industry benchmarks; v, various third-party integrations.. | Automated checks for inconsistencies, errors, outliers; data cleansing procedures | Standard reports, interactive dashboards, customizable visualizations | Highly customizable dashboards and reports; tailored to specific needs and stakeholder perspectives |
| Software A | Limited internal databases, specific industry benchmarks | Basic validation checks; manual data cleansing | Standard reports only | Limited customization options |
| Software B | Internal databases, limited third-party integrations | Automated validation checks; basic data cleansing | Standard reports, some interactive dashboards | Moderate customization options |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Specific features and capabilities may vary based on the chosen software solution and the chosen plan.
Benefits and Advantages
Implementing IBM ESG software offers a comprehensive suite of advantages for organizations seeking to enhance their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. This software streamlines data collection, analysis, and reporting, empowering companies to make more informed decisions and demonstrate their commitment to ESG principles. The system fosters transparency and accountability, ultimately leading to improved stakeholder relationships and potentially higher investor confidence.
Key Advantages of Adopting IBM ESG Software
This software provides a structured framework for organizations to effectively manage and improve their ESG performance. By centralizing data and providing comprehensive insights, the software helps companies identify areas for improvement, track progress, and communicate their ESG initiatives more effectively. This strategic approach strengthens the organization’s ability to respond to changing ESG priorities and stakeholder expectations.
- Enhanced Transparency and Accountability: The software facilitates transparent data collection and reporting, enabling companies to demonstrate their commitment to ESG principles. This transparency fosters trust among stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees. Detailed reports and dashboards provide a clear picture of ESG performance, allowing for easy identification of strengths and weaknesses, ultimately leading to greater accountability.
- Improved Decision-Making: IBM ESG software provides access to comprehensive ESG data, empowering organizations to make more informed decisions. The software allows for a sophisticated analysis of ESG performance, revealing trends and patterns that can inform strategic decisions. For example, an analysis of energy consumption patterns can identify areas for efficiency improvements, leading to reduced costs and environmental impact. Analysis of supplier relationships can illuminate areas needing improvement in labor practices and ethical sourcing.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying and analyzing potential ESG risks, the software helps companies proactively mitigate these risks. The system enables the early detection of emerging risks and vulnerabilities, such as supply chain disruptions or reputational damage. This allows organizations to develop appropriate risk mitigation strategies and avoid potential financial and reputational harm. For example, the software might highlight inconsistencies in a company’s supplier network, indicating a potential risk related to labor standards or environmental regulations.
- Improved Stakeholder Relationships: The software enables organizations to communicate their ESG performance effectively to stakeholders. Clear and concise reporting facilitates better engagement with investors, customers, and other stakeholders, fostering stronger relationships and building trust. This transparency can enhance a company’s reputation and attract environmentally and socially conscious investors.
Case Studies of Positive Impact
Numerous organizations have leveraged IBM ESG software to achieve significant improvements in their ESG performance and financial outcomes. These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of using the software, providing evidence of its effectiveness. For instance, a major manufacturing company using the software reduced its carbon emissions by 15% within the first year of implementation, resulting in significant cost savings and a positive impact on its reputation.
- XYZ Corporation: XYZ Corporation, a global retailer, implemented IBM ESG software to improve its supply chain sustainability. The software helped them identify suppliers with poor labor practices and enabled them to transition to more ethical suppliers, boosting their brand reputation and reducing reputational risks.
- ABC Industries: ABC Industries, a large energy company, used IBM ESG software to track and analyze its environmental footprint. The software helped them identify areas for efficiency improvements in their energy consumption, leading to cost savings and reduced carbon emissions. This resulted in a demonstrably positive impact on their environmental performance.
Key Benefits Summarized
The benefits of adopting IBM ESG software are numerous and substantial. This software empowers organizations to effectively manage their ESG initiatives and improve their overall performance. The table below summarizes the key advantages.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | By optimizing resource utilization, improving efficiency, and mitigating risks, the software can lead to substantial cost savings. Examples include reduced energy consumption, improved supply chain management, and reduced regulatory fines. |
| Risk Mitigation | The software proactively identifies and analyzes potential ESG risks, allowing for the development of appropriate mitigation strategies, avoiding reputational damage and financial losses. |
| Improved Reputation | Demonstrating a commitment to ESG principles through transparent reporting and consistent action enhances a company’s reputation, attracting environmentally and socially conscious investors, customers, and employees. |
| Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement | Facilitating clear and concise communication of ESG performance to stakeholders fosters stronger relationships and builds trust. |
Implementation and Integration
Implementing IBM ESG software within an organization requires a structured approach, considering the specific needs and existing infrastructure. Careful planning and execution are crucial for a successful transition, ensuring the software effectively integrates into the workflow and delivers anticipated benefits.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
A phased implementation approach is recommended for optimal results. The initial phase focuses on assessment and planning, followed by configuration and testing. A final deployment phase ensures smooth integration and user adoption. Detailed project plans, timelines, and resource allocation are critical to this process.
Necessary Resources and Expertise
Successful implementation hinges on having the right resources. This includes dedicated project managers, technical specialists familiar with the software, and subject matter experts who understand the organization’s ESG data. Adequate training for end-users is essential for successful adoption and utilization of the system.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integration with existing enterprise systems is a key consideration. Careful planning and design are essential to ensure seamless data flow. This might involve API integrations, data mapping, and system configuration adjustments. The process should be evaluated and documented thoroughly.
Customization Options
IBM ESG software offers customizable options to align with specific business needs. This allows tailoring reports, dashboards, and data visualizations to meet unique reporting requirements. The customization process should be carefully managed to maintain data integrity and system stability. Thorough documentation of customizations is vital.
Integration Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the process of integrating IBM ESG software with an existing system:
Start
|
V
Assess Existing Systems
|
V
Define Data Mapping Requirements
|
V
Configure API Integrations (if needed)
|
V
Test Data Migration & Validation
|
V
Deploy IBM ESG Software
|
V
User Training & Documentation
|
V
Monitor System Performance & Functionality
|
V
Iterate & Refine (as needed)
|
V
End
Data Migration Strategy
A well-defined data migration strategy is paramount. This involves a comprehensive plan for transferring data from existing systems to the IBM ESG software. The strategy should include data cleansing, validation, and transformation steps to ensure data quality and accuracy. This phase is crucial to maintaining data integrity and ensuring accurate reporting.
Future Trends and Developments

Source: planetcompliance.com
The ESG landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by increasing investor demand for transparency and accountability. This necessitates continuous adaptation for ESG reporting software solutions. IBM ESG software is positioned to address these evolving needs, leveraging advancements in data analytics and AI.
The future of ESG reporting hinges on seamless data integration, sophisticated analytics, and user-friendly reporting interfaces. IBM is strategically developing its platform to meet these demands, fostering a more comprehensive and actionable approach to ESG initiatives.
Emerging Trends in ESG Reporting
Advancements in AI-powered data analysis are transforming ESG reporting. Sophisticated algorithms can now identify patterns and anomalies in vast datasets, enabling more accurate and insightful assessments of environmental, social, and governance performance. This trend is crucial for companies striving to improve their ESG profiles and meet evolving regulatory requirements. Machine learning models can predict future ESG risks and opportunities, enabling proactive risk management strategies.
Adaptation of IBM ESG Software
IBM’s ESG software is actively adapting to these trends by integrating AI-driven analytical tools into its platform. This allows for enhanced data processing, providing more accurate insights into ESG performance. The platform is designed to seamlessly integrate with existing enterprise systems, minimizing data silos and maximizing efficiency. IBM is also enhancing its reporting capabilities to present complex ESG data in a clear, concise, and actionable manner, catering to the needs of diverse stakeholders.
Potential Future Developments in IBM ESG Software
Future releases of IBM ESG software will likely include more sophisticated AI-driven risk assessment modules. These modules will analyze vast datasets to identify potential ESG risks and opportunities, helping organizations develop proactive mitigation strategies. Real-time dashboards and interactive visualizations will enable users to monitor key ESG metrics and trends dynamically and engagingly. Enhanced data integration capabilities will allow for seamless connections with diverse data sources, providing a more holistic view of an organization’s ESG performance.
Innovative Features in Future Releases
A key feature in future releases will be enhanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities. This will allow for the automated extraction of ESG-related information from unstructured data sources, such as company reports and news articles. This automation will significantly reduce manual data entry and processing time while improving the accuracy and completeness of ESG data.
Further, advanced data visualization tools will allow users to easily create and share interactive dashboards showcasing key ESG metrics. These dashboards will provide a dynamic view of ESG performance over time, enabling better trend analysis and informed decision-making.
Advancements in ESG Data Collection and Analysis
Advancements in ESG data collection are focusing on greater standardization and accessibility. Open-source data platforms and industry collaborations are facilitating the development of common data formats and metrics. This standardization improves data comparability across organizations and industries, making it easier to benchmark performance.
Advanced data analysis techniques, such as predictive modeling and scenario planning, are being increasingly used to evaluate the long-term impact of ESG initiatives. This predictive capability is crucial for informed decision-making and strategic planning in an evolving ESG landscape. IBM ESG software will incorporate these advancements to offer comprehensive and insightful analyses.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, IBM ESG software offers a robust and comprehensive solution for managing ESG data and reporting. The software’s features, including data collection, analysis, and reporting capabilities, support organizations in achieving greater transparency and accountability in their ESG efforts. By providing actionable insights and enabling effective integration with existing systems, the software empowers companies to make informed decisions and improve their overall sustainability performance. This software is a key asset in today’s ESG-focused business landscape.